1 unstable release
| 0.1.0 | Dec 20, 2024 |
|---|
#742 in Algorithms
4KB
ZKP Fiat-Shamir Library
This Rust library implements the Fiat-Shamir heuristic to enable non-interactive Zero-Knowledge Proofs (NIZK). It provides a modular implementation for proving knowledge of a discrete logarithm (DLOG) without revealing the secret value.
What is the Fiat-Shamir Heuristic?
The Fiat-Shamir heuristic is a cryptographic technique that transforms an interactive Zero-Knowledge Proof (ZKP) into a non-interactive proof. Instead of requiring interaction between the Prover and Verifier, it uses a cryptographic hash function to simulate the Verifier's random challenges. This makes the proof compact and suitable for use in decentralized systems like blockchains.
Process of Fiat-Shamir Heuristic
- Commitment: The Prover generates a commitment based on a secret value and sends it to the Verifier.
- Challenge: In an interactive proof, the Verifier would send a random challenge. Using the Fiat-Shamir heuristic, this challenge is replaced by a hash of the commitment and other public parameters.
- Response: The Prover computes a response using the secret value, the commitment, and the challenge.
- Verification: The Verifier uses the public parameters, commitment, challenge, and response to verify the proof.
This approach ensures the proof remains secure, non-interactive, and zero-knowledge.
For a detailed explanation, watch this Fiat-Shamir tutorial.
Features
- Modular Exponentiation
- SHA-256-based Fiat-Shamir Challenge Generation
- Proof Generation and Verification for Discrete Logarithms (DLOG)
How to Use
Public API
-
Generate Commitment:
let t = generate_commitment(g, r, p);g: Generatorr: Random valuep: Modulus
-
Generate Challenge:
let c = generate_challenge(t, y, g, p);t: Commitmenty: Public value computed asy = g^x mod p
-
Generate Response:
let s = generate_response(r, c, x, p);r: Random valuec: Challengex: Secret value
-
Verify Proof:
let valid = verify_proof(t, y, g, s, c, p);- Returns
trueif the proof is valid,falseotherwise.
- Returns
Example
use zkp_fiat_shamir_lib::*;
fn main() {
let g = 5; // Generator
let p = 23; // Modulus
let x = 7; // Prover's secret
let y = mod_exp(g, x, p); // Public value
let r = 33; // Random commitment value
let t = generate_commitment(g, r, p);
let c = generate_challenge(t, y, g, p);
let s = generate_response(r, c, x, p);
if verify_proof(t, y, g, s, c, p) {
println!("Proof verified!");
} else {
println!("Invalid proof.");
}
}
Explaining the Process Diagram
The following diagram illustrates the process of the Fiat-Shamir Zero-Knowledge Proof, detailing the roles of the Prover and Verifier, along with the flow of communication and computation.
Diagram
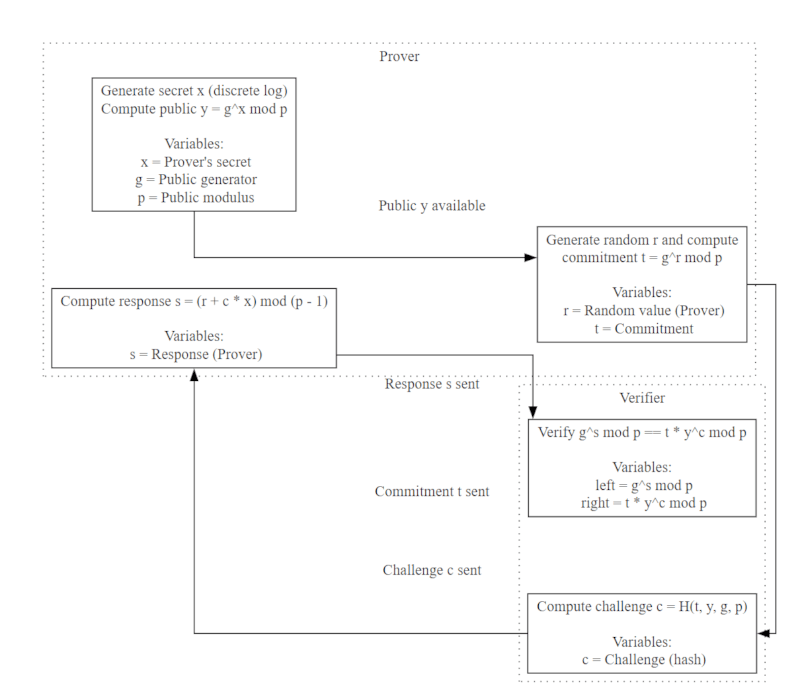
DOT Source Code for Diagram
If you wish to regenerate the diagram, here is the Graphviz DOT source:
digraph {
nodesep=1 rankdir=LR ranksep=1 splines=ortho
P1 [label="Generate secret x (discrete log)\nCompute public y = g^x mod p\n\nVariables:\n x = Prover's secret\n g = Public generator\n p = Public modulus" shape=box]
P2 [label="Generate random r and compute\ncommitment t = g^r mod p\n\nVariables:\n r = Random value (Prover)\n t = Commitment" shape=box]
P3 [label="Compute response s = (r + c * x) mod (p - 1)\n\nVariables:\n s = Response (Prover)" shape=box]
V1 [label="Compute challenge c = H(t, y, g, p)\n\nVariables:\n c = Challenge (hash)" shape=box]
V2 [label="Verify g^s mod p == t * y^c mod p\n\nVariables:\n left = g^s mod p\n right = t * y^c mod p" shape=box]
P1 -> P2 [label="Public y available"]
P2 -> V1 [label="Commitment t sent"]
V1 -> P3 [label="Challenge c sent"]
P3 -> V2 [label="Response s sent"]
subgraph cluster_Prover {
label=Prover style=dotted
P1
P2
P3
}
subgraph cluster_Verifier {
label=Verifier style=dotted
V1
V2
}
}
You can use this source code with any Graphviz-compatible tool to regenerate the diagram.
Installation
Add this crate to your Cargo.toml:
[dependencies]
zkp_fiat_shamir_lib = "0.1.0"
License
This project is licensed under the MIT License. See the LICENSE file for details.
Resources
- Tutorial on Fiat-Shamir Heuristic: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=n2WUJyk9cHA
Dependencies
~730KB
~18K SLoC