7 releases
| new 0.2.4 | Apr 3, 2025 |
|---|---|
| 0.2.3 | Apr 3, 2025 |
| 0.2.2 | Mar 31, 2025 |
| 0.1.1 | Mar 29, 2025 |
#156 in Programming languages
455 downloads per month
110KB
312 lines
Wave Serialization Object Notation
WSON (Wave Serialized Object Notation) is the default data serialization format for the Wave programming language, designed to overcome the limitations of traditional JSON while providing enhanced functionality and efficiency. WSON maximizes performance while maintaining a human-readable and writable structure, enabling faster and safer data exchange across various environments.
📄 Full syntax documentation: https://wave-lang.dev/docs/wson/
Installation
[dependencies]
wson_rs = "0.2.4"
Features
1. Strict Type System
WSON maintains clear data types, eliminating the unpredictability caused by JSON's dynamic typing. This ensures type safety during serialization and deserialization.
2. High Performance
WSON is designed with minimal overhead, offering fast data processing speeds. This is particularly effective when serializing large amounts of data.
3. Wave-Friendly Design
WSON is designed to integrate seamlessly with the Wave programming language and is natively supported by the standard Wave library.
4. Readability and Easy Parsing
While maintaining a syntax similar to JSON, WSON allows for more concise expressions, making it easier for humans to read and modify. Additionally, it has been optimized for efficient parsing.
5. Support for Various Data Structures
WSON supports not only simple key-value pairs but also complex data structures like native arrays, structs, and tuples, enabling more flexible data representation.
📚 Example
vex.ws (WSON format):
{
name = "wave_project",
version = 0.1.0,
lib = true,
dependencies = [
{ name = "core", version = 1.0.0 },
{ name = "wson", version = 0.1.1 }
]
}
Rust usage with wson_rs:
use wson_rs::{loads, dumps, validate, WsonValue};
fn main() {
let content = std::fs::read_to_string("vex.ws").unwrap();
if validate(&content) {
let data = loads(&content).unwrap();
if let Some(WsonValue::String(name)) = data.get("name") {
println!("Project name: {name}");
}
let serialized = dumps(&data).unwrap();
println!("Serialized WSON:\n{serialized}");
}
}
Benchmark
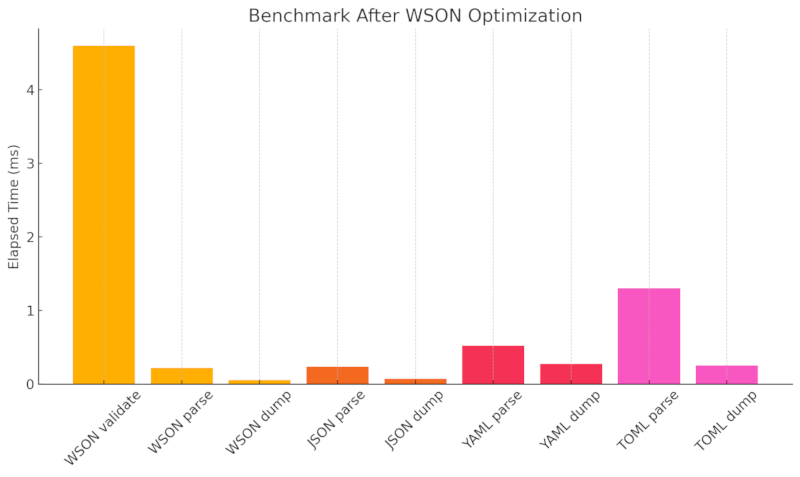
| Format | Operation | Elapsed Time (ms) |
|---|---|---|
| WSON | Validate | 4.604 |
| Parse | 0.219 | |
| Dump | 0.059 | |
| JSON | Parse | 0.239 |
| Dump | 0.072 | |
| YAML | Parse | 0.524 |
| Dump | 0.277 | |
| TOML | Parse | 1.306 |
| Dump | 0.254 |
📊 Benchmark results were generated using wson_rs v0.2.1 on a mid-range development machine.
Conclusion
WSON reflects the philosophy of the Wave language by aiming for more efficient and powerful data serialization. It addresses the shortcomings of traditional JSON while retaining an intuitive syntax, making it easier for developers to adopt.
Going forward, WSON will establish itself as the standard data format within the Wave ecosystem — clean, fast, and human-friendly.
📖 Read more at: https://wave-lang.dev/docs/wson/
Dependencies
~3–4.5MB
~72K SLoC