1 unstable release
| 0.6.0 | Feb 4, 2023 |
|---|---|
| 0.1.0 |
|
#512 in WebAssembly
220KB
5.5K
SLoC
wasmut
wasmut is a mutation testing tool for WebAssembly WASI modules.
Table of Content
- Installation
- Quick Start
- Command Line Interface
- WebAssembly Module Requirements
- Configuration File Reference
- Mutation Operators
- Author
- License
Installation
Currently, wasmut officially supports Linux and Windows. macOS should also
mostly work, however I cannot guarantee anything, since I do not have access to a Mac.
Pre-built binaries
For Linux and Windows, pre-built binaries for the amd64 architecture can be found on
the releases pages of this repository.
Installation using Cargo
wasmut is implemented in Rust, thus you need the Rust toolchain to compile the
project. The minimum supported Rust version (MSRV) is 1.67.
To install the latest wasmut release from crates.io run the following command:
> cargo install wasmut
This will install wasmut to $HOME/.cargo/bin by default. Make sure that
this path is included in our $PATH variable.
Development
If you want to hack on wasmut, simply check out the repository. Be sure to include
the testdata submodule.
> git clone --recursive https://github.com/lwagner94/wasmut
Once the repository is cloned, you can run the test-suite using the
test command.
cargo test
You may want to run wasmut as a release build. In development builds,
running mutants takes a a lot more time.
cargo run --release -- mutate testdata/simple_go/test.wasm -C
You can use the coverage.sh script to generate
a test-coverage report. Make sure that grcov and the nightly version of the Rust compiler are installed.
./coverage.sh
Quick start
Once installed, you can start using wasmut. To start off, you can
try out some of the examples in the testdata folder.
If you want to use wasmut with any of your own modules,
please be sure to check out the WebAssembly Module Requirements chapter.
If you run the mutate command without any flags, wasmut
will try to load a file called wasmut.toml in the current
directory and will fall back to default options if it cannot find it.
> # Run wasmut using default options (no filtering, all operators)
> wasmut mutate testdata/simple_add/test.wasm
[INFO ] No configuration file found or specified, using default config
[INFO ] Using 8 workers
[INFO ] Generated 37 mutations
...
Using the -C/-c flags, you can instruct wasmut to load
a configuration file from a different path. The -C flag will try
to load wasmut.toml from the same directory as the module, while -c allows you to provide the full path to the configuration file.
> wasmut mutate testdata/simple_add/test.wasm -C
[INFO ] Loading configuration file from module directory: "testdata/simple_add/wasmut.toml"
[INFO ] Using 8 workers
[INFO ] Generated 1 mutations
[INFO ] Original module executed in 40 cycles
[INFO ] Setting timeout to 80 cycles
/home/lukas/Repos/wasmut/testdata/simple_add/simple_add.c:3:14:
KILLED: binop_add_to_sub: Replaced I32Add with I32Sub
return a + b;
^
ALIVE 0
TIMEOUT 0
ERROR 0
KILLED 1
Mutation score 100%
By default, wasmut will print the results to the console - as shown above.
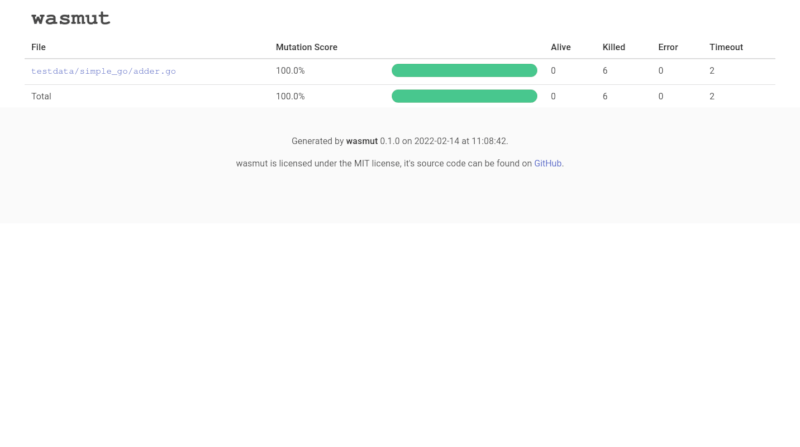
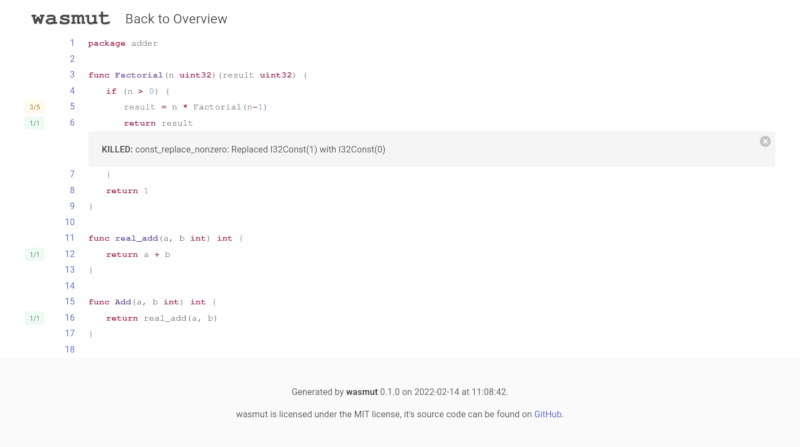
If you add the --report html option, wasmut will
create a HTML report in the wasmut-report folder.
> wasmut mutate testdata/simple_go/test.wasm -C --report html
[INFO ] Loading configuration file from module directory: "testdata/simple_go/wasmut.toml"
[INFO ] Using 8 workers
...
Command Line Interface
help
Display the help menu
list-files
List all files of the binary.
If a config is provided, this command will also show whether the file is allowed to be mutated. By
default, wasmut will try to load a wasmut.toml file from the current directory
USAGE:
wasmut list-files [OPTIONS] <WASMFILE>
ARGS:
<WASMFILE>
Path to the wasm module
OPTIONS:
-c, --config <CONFIG>
Load wasmut.toml configuration file from the provided path
-C, --config-samedir
Attempt to load wasmut.toml from the same directory as the wasm module
-h, --help
Print help information
-V, --version
Print version information
list-functions
List all functions of the binary.
If a config is provided, this command will also show whether the function is allowed to be mutated.
By default, wasmut will try to load a wasmut.toml file from the current directory
USAGE:
wasmut list-functions [OPTIONS] <WASMFILE>
ARGS:
<WASMFILE>
Path to the wasm module
OPTIONS:
-c, --config <CONFIG>
Load wasmut.toml configuration file from the provided path
-C, --config-samedir
Attempt to load wasmut.toml from the same directory as the wasm module
-h, --help
Print help information
-V, --version
Print version information
list-operators
List all available mutation operators.
If a config is provided, this command will also show whether the operator is enabled or not. By
default, wasmut will try to load a wasmut.toml file from the current directory
USAGE:
wasmut list-operators [OPTIONS] [WASMFILE]
ARGS:
<WASMFILE>
Path to the wasm module
OPTIONS:
-c, --config <CONFIG>
Load wasmut.toml configuration file from the provided path
-C, --config-samedir
Attempt to load wasmut.toml from the same directory as the wasm module
-h, --help
Print help information
-V, --version
Print version information
mutate
Generate and run mutants.
Given a (possibly default) configuration, wasmut will attempt to discover mutants and subsequently
execute them. After that, a report will be generated
USAGE:
wasmut mutate [OPTIONS] <WASMFILE>
ARGS:
<WASMFILE>
Path to the wasm module
OPTIONS:
-c, --config <CONFIG>
Load wasmut.toml configuration file from the provided path
-C, --config-samedir
Attempt to load wasmut.toml from the same directory as the wasm module
-h, --help
Print help information
-o, --output <OUTPUT>
Output directory for reports
[default: wasmut-report]
-r, --report <REPORT>
Report output format
[default: console]
[possible values: console, html]
-t, --threads <THREADS>
Number of threads to use when executing mutants
-V, --version
Print version information
new-config
Create new configuration file
USAGE:
wasmut new-config [PATH]
ARGS:
<PATH> Path to the new configuration file
OPTIONS:
-h, --help Print help information
-V, --version Print version information
run
Run module without any mutations
USAGE:
wasmut run [OPTIONS] <WASMFILE>
ARGS:
<WASMFILE> Path to the wasm module
OPTIONS:
-c, --config <CONFIG> Load wasmut.toml configuration file from the provided path
-C, --config-samedir Attempt to load wasmut.toml from the same directory as the wasm module
-h, --help Print help information
-V, --version Print version information
WebAssembly module requirements
wasmut currently supports WebAssembly modules using the WebAssembly System Interface (WASI).
wasmut will execute the _start function as an entry point into the module and will use the
module's exit code (set by the return value of main or explicit calls to exit) to determine the outcome
of the module's tests - 0 indicating success, and any non-zero exit code as a failure.
wasmut makes heavy use of DWARF debug information for mutant filtering and report
generation. Make sure to compile the WebAssembly module using the correct compiler flags
to ensure that debug information is embedded into the module.
Furthermore, compiler optimizations have a strong influence on wasmut's
performance. Some more experiments have to be done to give any recommendations,
but for now simply refer to the examples in the testdata directory
for any hints on what compiler options to use.
Configuration options
[engine] section
-
timeout_multiplier: Before executing mutants, wasmut will run the wasm module without any mutations and measure the number of cycles it takes to execute. Mutants then are allowed to execute with a timeout oftimeout = original_cycles * timeout_multipliertimeout_multiplier = 2.0 -
map_dirs: Map directories into the WebAssembly runtime. By default, modules cannot access the host's filesystem. If your module needs to access any files, you can use themap_dirsoption to define path mappings.# Map testdata/count_words/files to /files map_dirs = [["testdata/count_words/files", "files"],] -
coverage_based_execution: Before executing mutants, wasmut will run the wasm module without any mutations and generate coverage information. Ifcoverage_based_executionis enabled, the execution of mutants where the mutated instruction was never executed will be skipped. Defaults totrue.coverage_based_execution = true -
meta_mutant: Ifmeta_mutantis enabled, a single mutant containing all mutations will be generated. During execution, mutations are activated by setting a flag. The benefit of this is that only a single mutant needs to be compiled by the WebAssembly runtime, and thus the execution time is reduced significantly. Defaults totrue.meta_mutant = true
[filter] section
-
allowed_function/allowed_file: By default, all files and functions are allowed, which means that every WebAssembly instruction can potentially be mutated. This is not very practical, so it possible to specify and allowlist for functions and/or files. In allowed_functions and allowed_files, you can specify a list of regular expressions that are used to match the function and file names. A wasm-instruction is allowed to be mutated if its function or file matches at least one of the corresponding regular expressions. An empty regular expression also matches everything. Use thewasmut list-filesorwasmut list-functionscommands to get a list of all functions and files in the wasm module.allowed_functions = ["^add"] allowed_files = ["src/add.c", "src/main.c"]
[operators] section
-
enabled_operators: By default, all operators are allowed. If this is not what you want, you can use the enabled_operators option to specify which operators should be enabled. The option is a list of regular expressions. Use thewasmut list-operatorscommand or consult the documentation to get a list of all operators.# Enable binop_sub_to_add and all relop_* operators enabled_operators = ["binop_sub_to_add", "relop"]
[report] section
-
path_rewrite: When rendering reports,wasmutneeds to have access to the original source files.wasmutuses DWARF debug information embedded in the WebAssembly modules to locate them. As DWARF embeds absolute paths for the source files into the module, it can be problematic if you want to want to create reports for WebAssembly modules that where build on another host. Thepath_rewriteoption allows to specify a regular expression and a replacement that will be applied to any source file path before creating the report. Internally, Rust'sRegex::replaceis used. Consult the documentation for any advanced replacement scenarios.# Replace /home/user/wasmut/ with "build" # e.g. /home/user/test/main.c -> # build/test/main.c path_rewrite = ["^/home/user/", "build"]
Full example
[engine]
timeout_multiplier = 4.0
map_dirs = [["testdata/count_words/files", "files"],]
coverage_based_execution = true
meta_mutant = true
[filter]
allowed_functions = ["^count_words"]
#allowed_files = [""]
[operators]
enabled_operators = ["binop_sub_to_add", "relop"]
[report]
path_rewrite = ["^.*/wasmut/", ""]
Supported Mutation operators
The mutation operators available in wasmut are for now mainly based on mull's operators
| Name | Description |
|---|---|
binop_sub_to_add |
Replace subtraction with addition |
binop_add_to_sub |
Replace addition with subtraction |
binop_mul_to_div |
Replace multiplication with signed/unsigned division |
binop_div_to_mul |
Replace signed/unsigned division by multiplication |
binop_shl_to_shr |
Replace bitwise left-shift with signed/unsigned right-shift |
binop_shr_to_shl |
Replace signed/unsigned right-shift with left-shift |
binop_rem_to_div |
Replace remainder with division of the same signedness |
binop_div_to_rem |
Replace division with remainder of the same signedness |
binop_and_to_or |
Replace and with or |
binop_or_to_and |
Replace or with and |
binop_xor_to_or |
Replace xor with or |
binop_or_to_xor |
Replace or with xor |
binop_rotl_to_rotr |
Replace bitwise left-rotation with right-rotation |
binop_rotr_to_rotl |
Replace bitwise right-rotation with left-rotation |
unop_neg_to_nop |
Replace unary negation with nop |
relop_eq_to_ne |
Replace equality test with not-equal |
relop_ne_to_eq |
Replace not-equal test with equality |
relop_le_to_gt |
Replace less-equal with greater-than of the same signedness |
relop_le_to_lt |
Replace less-equal with less-than of the same signedness |
relop_lt_to_ge |
Replace less-than with greater-equal of the same signedness |
relop_lt_to_le |
Replace less-than with less-equal of the same signedness |
relop_ge_to_gt |
Replace greater-equal with greater-than of the same signedness |
relop_ge_to_lt |
Replace greater-than with less-than of the same signedness |
relop_gt_to_ge |
Replace greater-than with greater-equal of the same signedness |
relop_gt_to_le |
Replace greater-than with less-equal of the same signedness |
const_replace_zero |
Replace zero constants with 42 |
const_replace_nonzero |
Replace non-zero constants with 0 |
call_remove_void_call |
Remove calls to functions that do not have a return value |
call_remove_scalar_call |
Remove calls to functions that return a single scalar with the value of 42 |
Authors
wasmut was developed by Lukas Wagner.
License
Copyright © 2021-2022 Lukas Wagner.
All code is licensed under the MIT license. See LICENSE.txt file for more information.
Dependencies
~31–43MB
~738K SLoC