31 releases (19 stable)
Uses new Rust 2024
| 1.6.1 | Feb 20, 2025 |
|---|---|
| 1.4.0 | Dec 29, 2024 |
| 1.3.6 | Nov 21, 2024 |
| 1.3.5 | Jun 6, 2024 |
| 0.4.2 | Apr 23, 2020 |
#249 in Command line utilities
97 downloads per month
230KB
691 lines
nomino
Batch rename utility for developers
How to install
Pre-Compiled
You can download a pre-compiled executable for Linux, MacOS and Windows operating systems, then you should copy that executable to a location from your $PATH env:
You might need to run chmod +x nomino-linux-64bit or chmod +x nomino-macos-64bit.
Build Manually
If you prefer to build nomino manually, or a pre-compiled executable is not provided for your target, then you can build nomino from scratch:
- Install Rust:
curl -sSf https://sh.rustup.rs | sh - Run
cargo install nomino
Usage
Usage:
nomino [OPTIONS] [[SOURCE] OUTPUT]...
Arguments:
[[SOURCE] OUTPUT]...
OUTPUT is the pattern to be used for renaming files, and SOURCE is the optional regex pattern to match by filenames. SOURCE has the same function as -r option
Options:
-d, --dir <PATH> Sets the working directory
--depth <DEPTH> Optional value to overwrite inferred subdirectory depth value in 'regex' mode
-E, --no-extension Does not preserve the extension of input files in 'sort' and 'regex' options
-g, --generate <PATH> Stores a JSON map file in '<PATH>' after renaming files
-h, --help Print help (see a summary with '-h')
-k, --mkdir Recursively creates all parent directories of '<OUTPUT>' if they are missing
-m, --map <PATH> Sets the path of map file to be used for renaming files
--from-file <PATH> Alias for --map
--max-depth <DEPTH> Optional value to set the maximum of subdirectory depth value in 'regex' mode
-q, --quiet Does not print the map table to stdout
-r, --regex <PATTERN> Regex pattern to match by filenames
-s, --sort <ORDER> Sets the order of natural sorting (by name) to rename files using enumerator
Possible ORDER values:
- asc: Sort in ascending order
- desc: Sort in descending order
-t, --test Runs in test mode without renaming actual files
--dry-run Alias for --test
-V, --version Print version
-w, --overwrite Overwrites output files, otherwise, a '_' is prepended to filename
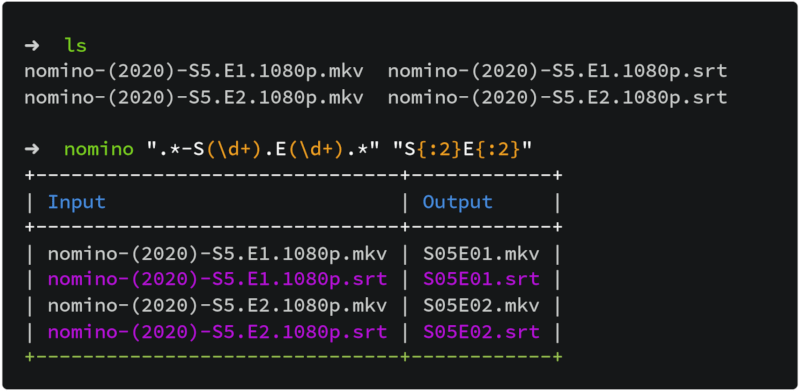
OUTPUT pattern accepts placeholders that have the format of '{G:P}' where 'G' is the captured group and 'P' is the padding of digits with `0`. Please refer to https://github.com/yaa110/nomino for more information.
Placeholders
- Placeholders have the format of
{G:P}whereGis the captured group andPis the padding of digits with0. For example,{2:3}means the third captured group with a padding of 3, i.e.1is formatted as001. - Indices start from
0, and{0}means the filename. - The capture group
Gcould be dropped, i.e.{}or{:3}. In this case an auto incremental index is used which starts from1. For example,{} {}equals{1} {2}. {and}characters could be escaped using\character, i.e.\\{and\\}in cli.- Padding is only used for positive numbers, e.g. the formatted result of
{:3}for1is001, for-1is-1and foraisa. - If
--sortoption is used, the first index{0}is the filename and the second index{1}or first occurrence of{}is the enumerator index.
Capture Groups
The accepted syntax of regex pattern is Rust Regex.
Consider this example:
(?<first>\w)(\w)\w(?<last>\w)
This regular expression defines 4 capture groups:
- The group at index
0corresponds to the overall match. It is always present in every match and never has a name:{0}. - The group at index
1with namefirstcorresponding to the first letter:{1},{first}or the first occurrence of{}. - The group at index
2with no name corresponding to the second letter:{2}or the second occurrence of{}. - The group at index
3with namelastcorresponding to the fourth and last letter:{3},{last}or the third occurrence of{}.
?<first> and ?<last> are named capture groups.
Windows
On Windows, \\ must be used to separate path components in file paths because \ is a special character in regular expressions.
Map file format
{
"<input1>": "<output1>",
"<input2>": "<output2>",
"<...>": "<...>"
}
Wiki
Dependencies
~6–15MB
~177K SLoC