4 stable releases
| 1.0.3 | Jun 19, 2020 |
|---|---|
| 1.0.1 | Jun 18, 2020 |
#445 in Machine learning
185KB
2.5K
SLoC
l2 • 🤖
A Pytorch-style Tensor+Autograd library written in Rust
Installation • Contributing • Authors • License • Acknowledgements
Made by Bilal Khan • https://bilal.software
What is l2?
l2 is named after the l2 or Euclidean distance, a popular distance function in deep learning
l2 is a Pytorch-style Tensor+Autograd library written in Rust. It contains a multidimensional array class, Tensor, with support for strided arrays, numpy-style array slicing, broadcasting, and most major math operations (including fast, BLAS-accelerated matrix multiplication!). On top of this, l2 has a built-in efficient graph-based autograd engine that keeps track of all operations performed on a tensor and topologically sorts and traverses the graph to compute the gradients.
I also made a more simplified C++ version of l2 last year, which you can take a look at here
Quick start
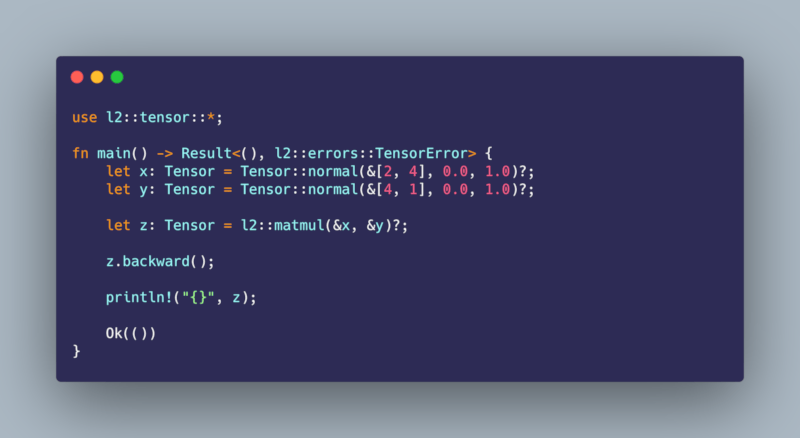
Add l2 = "1.0.3" to your Cargo.toml file and add the following to main.rs
use l2::tensor::*;
let x: Tensor = Tensor::normal(&[2, 4], 0.0, 1.0)?;
let y: Tensor = Tensor::normal(&[4, 1], 0.0, 1.0)?;
let z: Tensor = l2::matmul(&x, &y)?;
z.backward();
println!("{}", z);
Design choices
I made l2 to get better at using Rust and to learn more about how libraries like Pytorch and Tensorflow work behind the scenes, so don't expect this library to be production-ready :)
l2 is surprisingly fast especially since I didn't try very hard to optimize all the operators, it's usually only less than one order of magnitude slower than Pytorch in most of the benchmarks that I ran. l2 only supports a cpu backend at the moment since I'm not familiar enough with rust to start working with CUDA and cudnn. So far, l2 doesn't have any Pytorch-style abstractions like the Parameter, Layer, or Module classes. There might still be some bugs in the transpose operators and calling .backward() on tensors with more dimensions. I was interested in using Rust's Const Generics to run compile-time shape checks but I decided to leave it until some other time.
Contributing
This repository is still a work in progress, so if you find a bug, think there is something missing, or have any suggestions for new features, feel free to open an issue or a pull request. Feel free to use the library or code from it in your own projects, and if you feel that some code used in this project hasn't been properly accredited, please open an issue.
Authors
- Bilal Khan
License
This project is licensed under the MIT License - see the license file for details
Acknowledgements
The fast.ai deep learning from the foundations course (https://course.fast.ai/part2) teaches a lot about how to make your own deep learning library
Some of the resources that I found useful when working on this library include:
- http://blog.ezyang.com/2019/05/pytorch-internals/
- https://pytorch.org/tutorials/beginner/nn_tutorial.html
- https://eisenjulian.github.io/deep-learning-in-100-lines/
- https://medium.com/@florian.caesar/how-to-create-a-machine-learning-framework-from-scratch-in-491-steps-93428369a4eb
- https://medium.com/@johan.mabille/how-we-wrote-xtensor-1-n-n-dimensional-containers-f79f9f4966a7
- https://erikpartridge.com/2019-03/rust-ml-simd-blas-lapack
- https://medium.com/@GolDDranks/things-rust-doesnt-let-you-do-draft-f596a3c740a5
- https://datascience.stackexchange.com/questions/20139/gradients-for-bias-terms-in-backpropagation
- https://cs231n.github.io/optimization-2/
- https://cs231n.github.io/neural-networks-case-study/#grad
- https://stackoverflow.com/questions/38082835/backpropagation-in-gradient-descent-for-neural-networks-vs-linear-regression
- https://medium.com/@karpathy/yes-you-should-understand-backprop-e2f06eab496b
- https://stackoverflow.com/questions/38082835/backpropagation-in-gradient-descent-for-neural-networks-vs-linear-regression
- https://github.com/karpathy/micrograd
- https://rufflewind.com/2016-12-30/reverse-mode-automatic-differentiation
- https://discuss.pytorch.org/t/is-pytorch-autograd-tape-based/13992/3
- https://www.reddit.com/r/MachineLearning/comments/8ep130/d_how_does_autograd_work/
- https://github.com/mattjj/autodidact
- https://github.com/karpathy/recurrentjs
- https://github.com/karpathy/randomfun
- https://medium.com/@ralphmao95/simple-autograd-implementation-understand-automatic-differentiation-hand-by-hand-9e86f6d703ab
- https://evcu.github.io/ml/autograd/
- https://blog.paperspace.com/pytorch-101-understanding-graphs-and-automatic-differentiation/
- https://github.com/maciejkula/wyrm
- https://medium.com/@maciejkula/building-an-autodifferentiation-library-9ccf32c7a658
- https://github.com/evcu/numpy_autograd/blob/master/my_autograd.py#L147
- https://github.com/evcu/numpy_autograd/blob/master/Autograd.ipynb
- https://cs231n.github.io/optimization-2/
- https://github.com/explosion/thinc
- https://github.com/joelgrus/joelnet
- https://github.com/QuantStack/xtensor
- https://github.com/ThinkingTransistor/Sigma
- https://github.com/mratsim/Arraymancer
- https://github.com/siekmanj/sieknet
- https://github.com/siekmanj/sieknet_2.0
- https://github.com/Daniel-Liu-c0deb0t/Java-Machine-Learning
- https://github.com/karpathy/micrograd
This README is based on:
- https://github.com/bkkaggle/pytorch_zoo
- https://github.com/bkkaggle/grover
- https://github.com/rish-16/gpt2client
- https://github.com/mxbi/mlcrate
- https://github.com/athityakumar/colorls
- https://github.com/amitmerchant1990/electron-markdownify
I used carbon.now.sh with the "Shades of Purple" theme for the screenshot at the beginning of this README
This project contains ~4300 lines of code
Dependencies
~2–2.7MB
~52K SLoC