18 unstable releases (4 breaking)
| 0.5.0 | Aug 20, 2024 |
|---|---|
| 0.4.1 | Apr 29, 2024 |
| 0.4.0 | Jan 8, 2024 |
| 0.3.2 | Dec 4, 2023 |
| 0.1.1 | Jul 27, 2023 |
#251 in Asynchronous
188 downloads per month
Used in 3 crates
10MB
1K
SLoC
keen-retry
Introduction
The keen-retry crate is designed to provide a zero-cost, flexible, and robust way to implement retry logic in Rust applications, while also
supporting adding resiliency to libraries. Whether you are developing an API, a high-performance system, a distributed application, or a simple
tool, keen-retry offers a comprehensive set of features to handle transient failures gracefully, ensuring your application remains resilient,
reliable and is able to provide rich diagnostic messages, indispensable for addressing the root cause of failures.
Features
- Zero-Cost Abstraction: Leverages Rust's powerful type system and compile-time optimizations to offer retry capabilities with no runtime overhead.
- Clear Error Discrimination: Retrying operations that fail due to non-transient errors is futile, can waste resources and may ruin the application performance.
- Instrumentation and Logging: Comprehensive logging and instrumentation features for observing and debugging retry operations.
- Composable Retry Logic: Easily chainable and composable retry operations, allowing for clean and maintainable code.
- Async/Await Support: First-class support for asynchronous programming, compatible with Tokio and other async runtimes.
- Flexible Backoff Strategies: Includes various backoff strategies, from simple constant delays to sophisticated exponential backoff with jitter, suitable for different scenarios and needs.
Quick Start
Integrate your Library / API
The first step is to have every retryable operation from your Library or API returning the enriched RetryResult type, which clearly discriminates between Ok, Fatal and Transient variants:
/// Wrapper around [Self::connect_to_server_raw()], enabling `keen-retry` on it
pub async fn connect_to_server(&self) -> RetryProcedureResult<ConnectionErrors> {
self.connect_to_server_raw().await
.map_or_else(|error| match error.is_fatal() {
true => RetryResult::Fatal { input: (), error },
false => RetryResult::Transient { input: (), error },
},
|_| RetryResult::Ok { reported_input: (), output: () })
}
Usage
Now, in the application, you may use it via the zero-cost functional API:
let resolved = connect_to_server()
.retry_with(|_| connect_to_server())
.<one-of-the-backoff-strategies>(...)
.<instrumentation-facilities>(...)
.<mapping-of-outputs-and-errors>(...);
The keen-retry Diagram
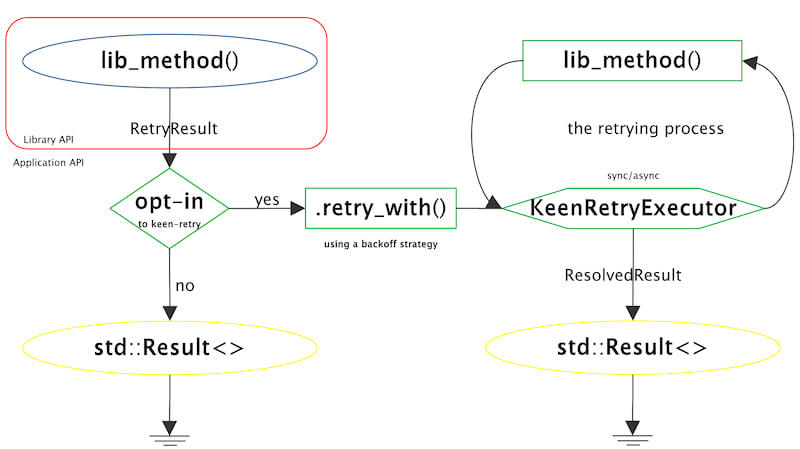
For more details, please refer to tests/use_cases.rs, which contains advanced
demonstrations such as how to add a fully fledged instrumentation (as seen in production applications),
how to compose nested retry logics and how to implement the versatile "Partial Completion with Continuation
Closure" design pattern.
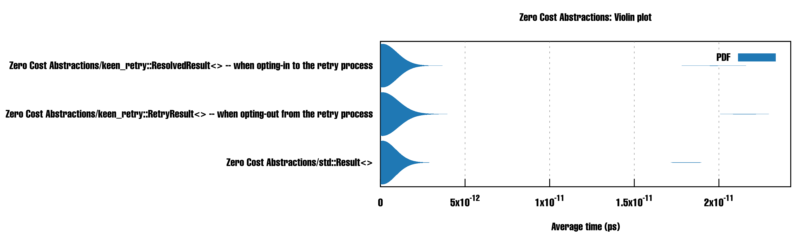
Performance Analysis
keen-retry has been rigorously benchmarked to ensure it adheres to the zero-cost abstraction principle, crucial in systems programming.
Our benchmarks, available at benches/zero_cost_abstractions.rs, demonstrate the efficiency of the crate.
The Book
For a deep dive into the applicable Design Patterns, principles, strategies, and best practices for using keen-retry effectively,
be sure to explore our companion keen-retry crate's Book, which serves as a definitive guide, providing insights and practical
examples to harness the full potential of keen-retry in various software development scenarios.
